Groundwater transmissivity calculator units: cm=centimeter, ft=foot, gpd=U.S. gallon/day, gph=U.S. gallon/hr, gpm=U.S. gallon/min, gal=gallon (U.S.), hr=hour, km=kilometer, m=meter, min=minute, s=second.
Groundwater Drawing and Transmissivity Equation
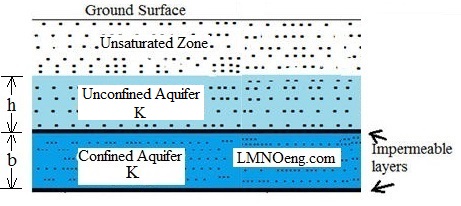
Unconfined Aquifer: T = K h
Confined Aquifer: T = K b
Groundwater transmissivity is a useful parameter in groundwater flow modeling.
Groundwater transmissivity includes the hydraulic conductivity which is a property of the aquifer.
Hydraulic conductivity is a function of the fluid moving through the porous medium (i.e. aquifer, formation)
and the permeability of the formation. Many experiments over many years
have been conducted of water flowing through various porous media.
Hydraulic conductivities determined from many experiments have been tabulated.
The table below is typical. In viewing the table, it is apparent that hydraulic
conductivity values cover a wide range even for a given formation. If field or
laboratory test results of hydraulic conductivity are not available for your
particular formation, then use of published values like the ones below are helpful guides.
In addition to hydraulic conductivity, groundwater transmissivity is a function of aquifer thickness.
In unconfined aquifers, the aquifer thickness is a height h. h is the water depth above
an impermeable boundary. If a well is pumped, h can vary with time and location.
In confined aquifers, the aquifer thickness b is independent of any effects of pumping since
the aquifer is bound between two impermeable layers. Water in a confined aquifer is under pressure between
the layers. If the water level drops below the upper impermeable layer, then the aquifer
would no longer be confined.
Hydraulic Conductivity Table (Freeze and Cherry, 1979, p. 29)
The values in the drop-down menu in our groundwater transmissivity calculator are typical numbers within the ranges given below for clayey, silty, sandy, and gravelly soil.
| Unconsolidated Deposits | Hydraulic Conductivity (m/s) |
| Unweathered Marine Clay | 10-12 - 10-9 |
| Glacial Till | 10-12 - 10-6 |
| Silt, Loess | 10-9 - 10-5 |
| Silty Sand | 10-7 - 10-3 |
| Clean Sand | 10-6 - 10-2 |
| Gravel | 10-3 - 1 |
Rocks |
|
| Unfractured Metamorphic and Igneous Rocks | 10-14 - 10-10 |
| Shale | 10-13 - 10-9 |
| Sandstone | 10-10 - 10-6 |
| Limestone and dolomite | 10-9 - 10-6 |
| Fractured Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks | 10-8 - 10-4 |
| Permeable Basalt | 10-7 - 10-2 |
| Karst Limestone | 10-6 - 10-2 |
Notation (SI units are shown. Groundwater transmissivity calculator allows variety of units)
b = Confined aquifer thickness (m).
h = Height of water table in unconfined aquifer (m).
K = Aquifer hydraulic conductivity (m/s).
T = Aquifer tranmssivity (m2/s).
Reference
Freeze, R. A. and Cherry, J. A. 1979. Groundwater. Prentice-Hall, Inc.
© 2017-2026 LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd. All rights reserved.
LMNO Engineering, Research, and Software, Ltd.
7860 Angel Ridge Rd. Athens, Ohio 45701 USA Phone: (740) 707-2614
LMNO@LMNOeng.com
https://www.LMNOeng.com
